Return to site
[VV121] The Java 21 Newsletter: 🔼 Upcasting and 🔽 Downcasting (Subcasting)
[VV121] The Java 21 Newsletter: 🔼 Upcasting and 🔽 Downcasting (Subcasting)
·
🔼 Upcasting
- Definition: Casting a subclass object to a superclass type.
- Safe: Always safe, no explicit cast required.
- What is accessible: Only the declared type’s methods/fields (superclass), unless overridden.
Key Point:
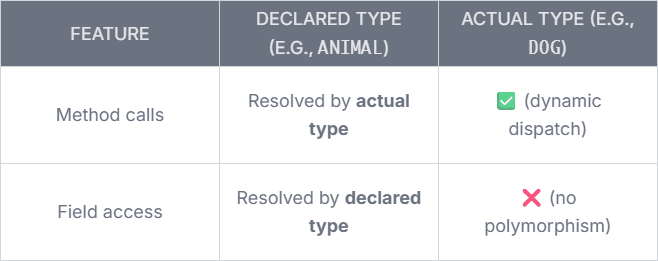
- ✅ Methods are determined at runtime → actual object's type (Dog) decides what method is executed (polymorphism).
- ❌ Attributes/fields (if any) are not polymorphic → they are resolved at compile-time using the declared type.
🔽 Downcasting (Subcasting)
- Definition: Casting a superclass object to a subclass type.
- Risky: Must be done explicitly, and it can throw a ClassCastException if not valid.
- What is accessible: After downcasting, you can access the subclass-specific methods/fields.
Wrong downcast example:
🔧 Summary Table
🔍 Real Example with Field
🎢 Mental Model: Think of a Class Hierarchy as a Tree
Object
- The top of the tree is more general (Object, Animal)
- The bottom of the tree is more specific (Dog, Poodle, etc.)
🔼 Upcasting = Going up the hierarchy
- From specific to general (e.g., Dog → Animal)
- Safe, because a Dog is always an Animal
- Loses access to specific features
🔽 Downcasting = Going down the hierarchy
- From general to specific (e.g., Animal → Dog)
- Risky, because not all Animals are Dogs
- Gains access to subclass features, but only if valid
🧠 How to Remember
Try one of these mnemonics:
1. "Upcasting climbs the tree, downcasting dives deep."
- Imagine the class hierarchy as a vertical structure (like a tree or org chart).
- "Up" means more general (e.g., to Animal or Object)
- "Down" means more specific (e.g., to Dog)
2. Think in terms of "zoom level":
- Upcasting = zooming out → you see less detail (fewer features)
- Downcasting = zooming in → you see more detail (more features, but may not always be safe)
3. Java's automatic vs. manual:
- Upcasting = automatic (Java does it for you)
- Downcasting = manual (you have to tell Java: Dog d = (Dog) a;)
🧪 Example Recap
Upcasting: Dog → Animal (safe, general)
Downcasting: Animal → Dog (risky, specific)
Upcasting: Dog → Animal (safe, general)
Downcasting: Animal → Dog (risky, specific)